Controlling Data Entry Using Form Fields
Creating 'Encoded' Name & Value Pairs
Passing data from one form to another
Addressing Form Field Validation with Regular Expressions and JavaScript 1.2
You are here: irt.org | Articles | JavaScript | Form | Chapter 6: Beginning JavaScript [ previous next ]
Published on: Sunday 29th April 2001 By: Paul Wilton
There are about ten elements commonly found within <FORM> elements. The most useful are shown below, ordered into general types. We give each its name and, in parentheses, the HTML needed to create it, though note this is not the full HTML but only a portion.
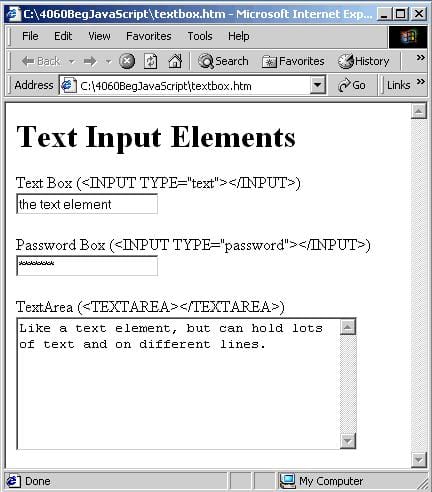
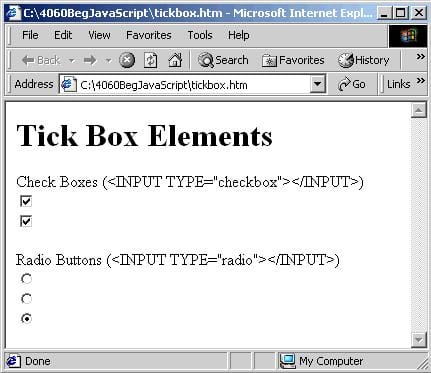
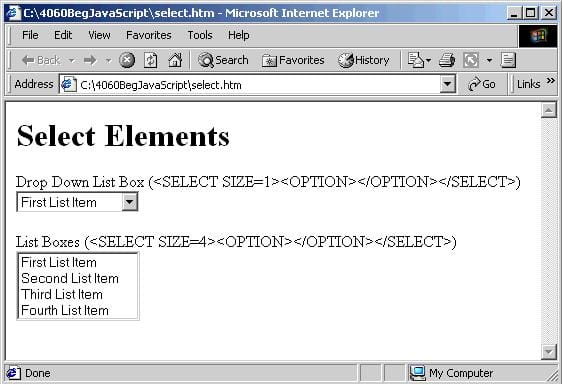
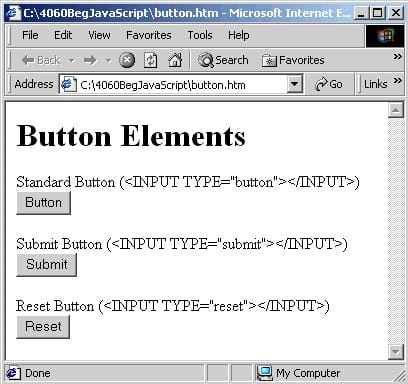
As you can see, most of the form elements are created using the <INPUT> tag. One of the <INPUT> tag's attributes is the TYPE attribute. It's this attribute that decides which of the HTML elements this will be. Examples of values for this attribute include button, to create a button, and text to create a text box.
Each form element inside the web page is made available to us as, yes, you guessed it, an object. As with all the other objects we have seen, each element's object has its own set of distinctive properties, methods and events. We'll be taking a look at each form element in turn and how to use its particular properties, methods, and events. But, before we do that, let's look at properties and methods that the objects of the form elements have in common.
Controlling Data Entry Using Form Fields
Creating 'Encoded' Name & Value Pairs
Passing data from one form to another
Addressing Form Field Validation with Regular Expressions and JavaScript 1.2